Dacryocystorhinostomy Surgery
What is Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery?
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery creates a bypass between the tear sac and nose by removing a small piece of bone normally wedged between them, and is performed either via the endonasal or external approaches.
External DCR Surgery
The traditional external approach is by making a 1-1.5cm skin incision on the side of your nose, where a pair of glasses would rest.
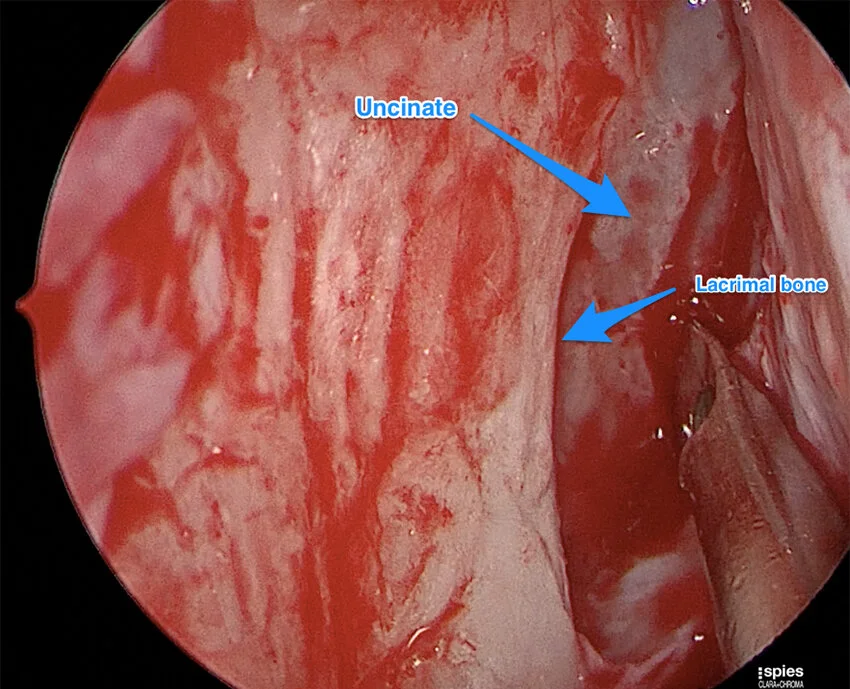
Endoscopic DCR Surgery
In the endoscopic (or endonasal) approach, surgery is performed inside the nose, thus avoiding a skin incision and potential external scarring.
What are the results of DCR surgery?
DCR surgery is 90-95% successful at improving the watery/sticky eyes, when there is a clear blockage.
The success rate is lower if there is no clear blockage demonstrated on syringing or on scans despite the presence of watery/sticky eyes.
There is no difference in success rates between external and endoscopic DCR.
What happens on the day of surgery?
The endoscopic DCR operation takes about an hour and is usually performed under a general anaesthetic, but external DCR is sometimes performed under local anaesthetic with intravenous sedation. In some patients, small silicon “tubes” are placed to keep the newly made passages open while healing takes place. These tubes are usually removed 4-6 weeks after surgery. The procedure is usually performed as a day procedure and patients are discharged the same day.
Eyelid Conditions & Treatments
Watery Eyes Conditions & Treatments
Dacryocystorhinostomy Surgery (DCR)
Orbital Conditions & Treatments
Medical Disclaimer
All content and media on this Website (www.dryechen.com) is created and published online for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice and should not be relied on as health or personal advice.
All photographs on this website of before and after results are examples only, and do not constitute an implied or any other kind of certainty for the result of surgery or a non-surgical procedure. All surgical and non-surgical results are subject to the individual results for the patient and the normal variability of clinical procedure results. All surgery and non-surgery procedures carry potential risks and complications which are described in detail in our surgical consent forms. All patients have given their consent for their images to be displayed on this Website.
Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. Never disregard the advice of a medical professional, or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this Website.
If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor, go to the nearest hospital emergency department, or call the emergency services immediately. If you choose to rely on any information provided by Dr Ye Chen, you do so solely at your own risk.
External (outbound) links to other websites or educational material (e.g. pdf’s etc…) that are not explicitly created by Dr Ye Chen are followed at your own risk. Under no circumstances is Dr Ye Chen responsible for the claims of third party websites or educational providers.
If you wish to seek clarification on the above matters please don’t hesitate to get in touch with Dr Ye Chen.